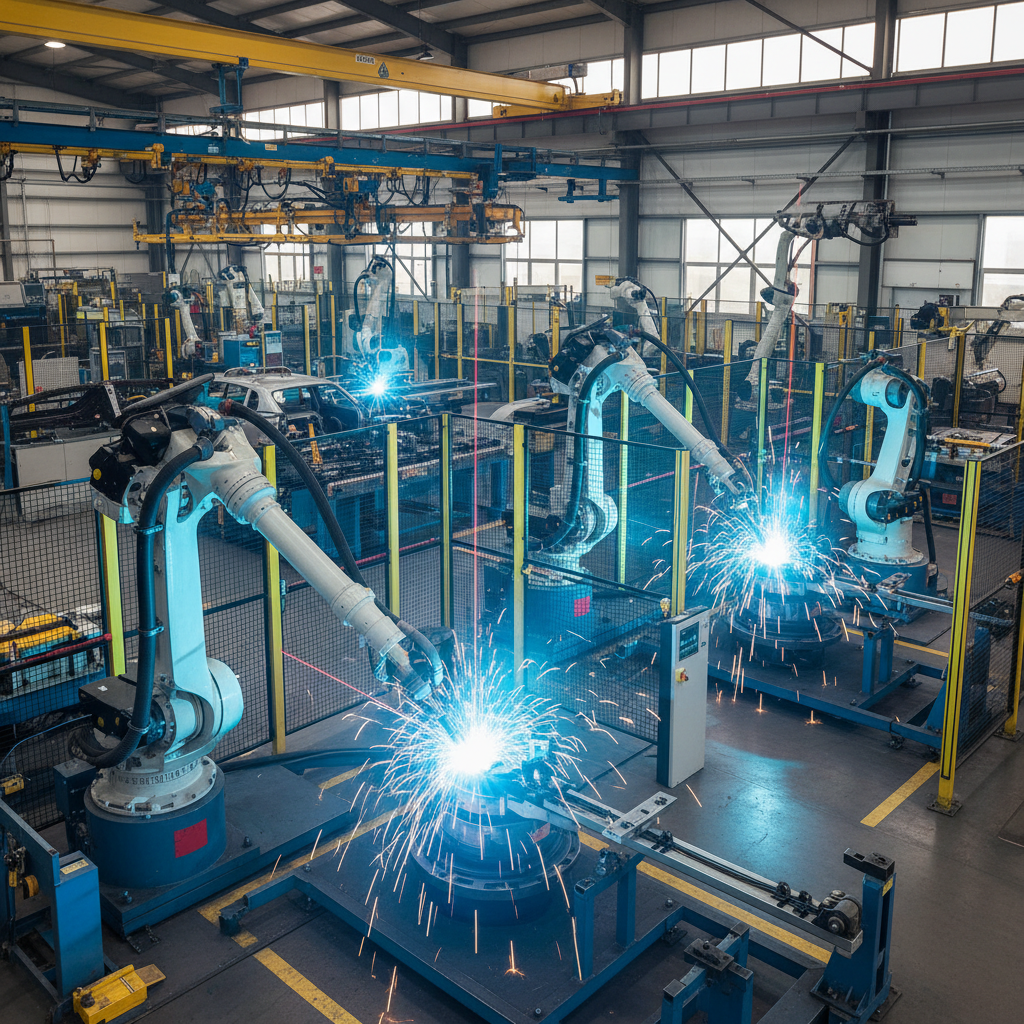
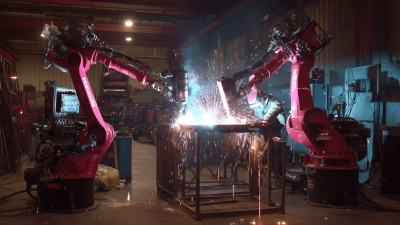
In recent years, the welding industry has been significantly transformed by advancements in technology, particularly through the integration of robotic welding. As highlighted by industry expert Dr. John Smith, a leading authority in automated manufacturing, “Robotic welding is not just the future of welding; it is the present driving efficiency, precision, and safety in fabrication processes.” This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of robotic welding, exploring its myriad advantages and potential applications across various sectors.
Robotic welding offers unparalleled consistency and speed, drastically reducing production times while maintaining high-quality standards. As manufacturers continuously seek ways to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs, the adoption of robotic welding systems becomes increasingly essential. This guide aims to equip readers with a thorough understanding of robotic welding technologies, the typical configurations used, and the critical factors to consider when implementing these systems into existing workflows.
By embracing robotic welding, companies can not only improve their competitive edge but also foster innovation within their production lines. As we explore this fascinating subject, it becomes clear that the future of welding lies in automation, and understanding robotic welding will be pivotal for businesses aspiring to thrive in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape.
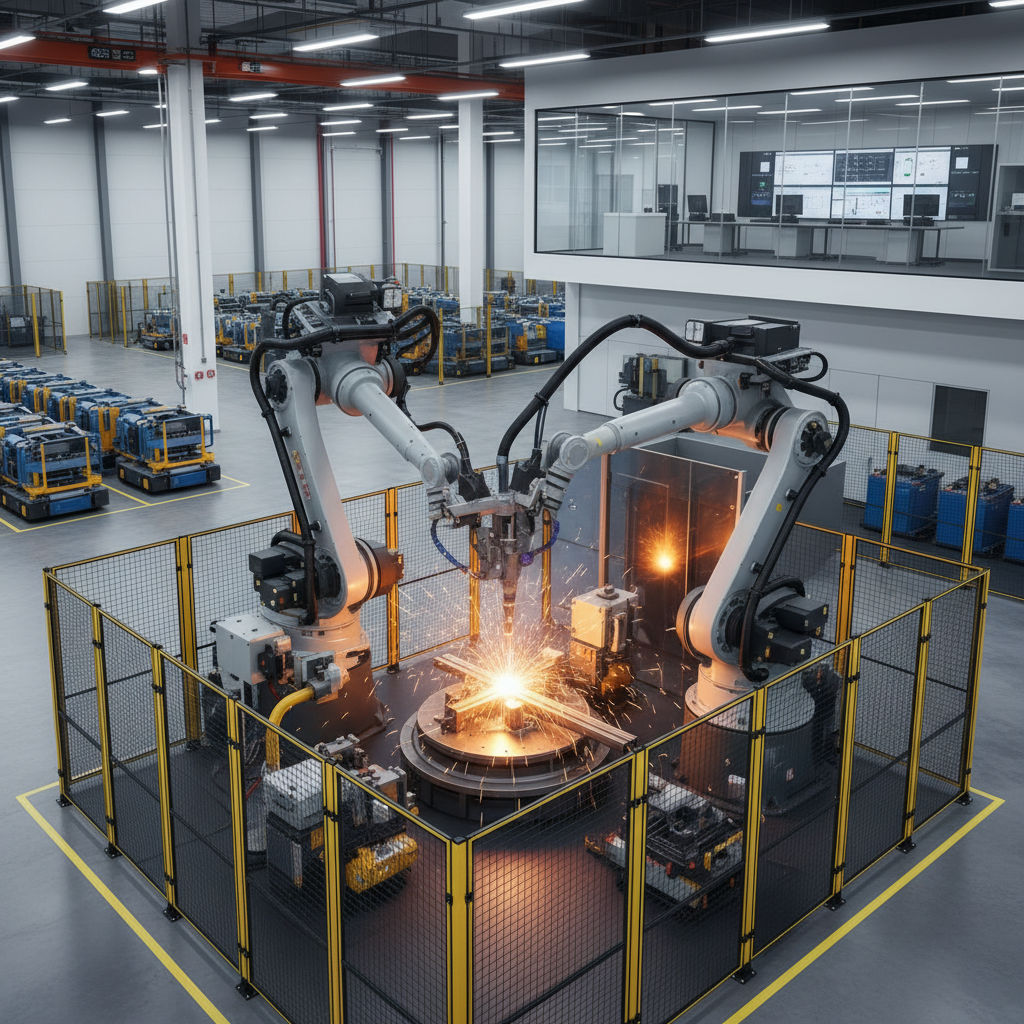

Robotic welding is an advanced technology that utilizes robotic systems to perform welding tasks with precision and efficiency. In essence, it refers to the automation of the welding process through programmed robots capable of executing complex welds without the need for direct human intervention. The key concepts related to robotic welding include the types of robots used, such as articulated robots, and the welding techniques employed, such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding.
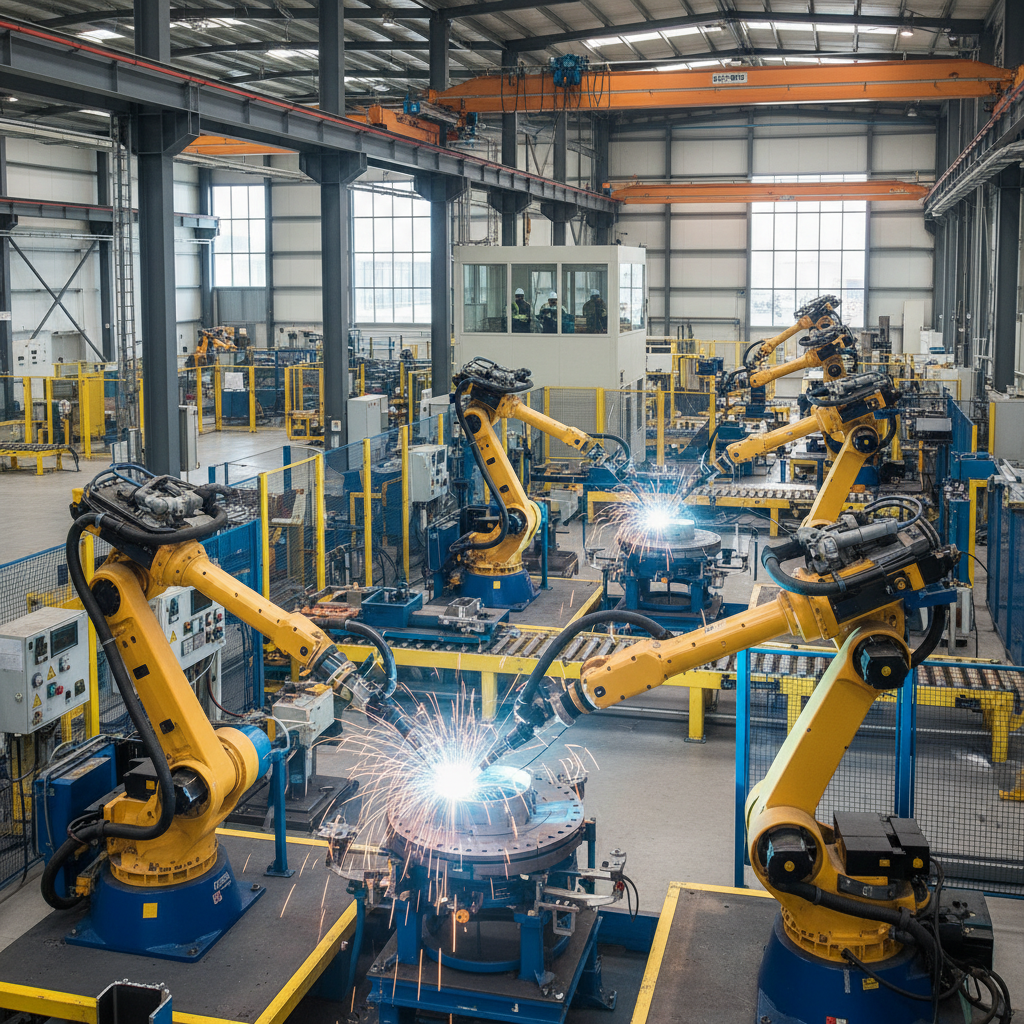

Understanding the components of robotic welding involves recognizing the significance of the control systems that guide the movement and operation of the robots. These systems enable accurate positioning and timing, which are crucial for achieving high-quality welds. Additionally, the integration of sensors and vision systems enhances the robots' ability to adapt to variations in workpieces, resulting in improved consistency and reduced defects in welded joints. As industries continue to embrace automation, robotic welding stands out as a transformative solution that increases production speed while maintaining superior quality standards.
Robotic welding is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering a host of advantages that enhance productivity and efficiency. With the global robotic welding market projected to grow significantly, from $8.1 billion in 2025 to $20.16 billion by 2032, businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of automating welding processes. This transformation is fueled by the need for precision and consistency in production, which can be achieved through robotic technologies that work tirelessly and accurately compared to traditional manual methods.
In addition to improving throughput, robotic welding integrates seamlessly with advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, which further optimizes operations and reduces costs. By employing AI-driven automation, manufacturers can adapt quickly to changing demands and enhance operational flexibility. The collaborative robots, or cobots, have emerged as a vital asset, often performing alongside human workers to take on repetitive tasks. This collaboration not only boosts efficiency but also allows human operators to focus on more complex, value-added activities, maximizing overall productivity in the manufacturing environment.
Robotic welding has become an essential part of modern manufacturing, offering advanced technologies that cater to a variety of applications. Among the leading types are arc welding, laser welding, and spot welding, each with its own set of advantages. Arc welding systems are widely used for their versatility and ability to weld thick materials, while laser welding provides precision and speed, making it ideal for intricate designs. Spot welding, often utilized in the automotive industry, allows for rapid joining of metal sheets, enhancing production efficiency.
Working with robotic welding systems comes with its own challenges, especially in complex environments that demand adaptability and precision. To navigate these challenges, companies can implement several strategies.
**Tips:** First, ensure that the robotic systems are equipped with sensors that can monitor real-time parameters, improving adaptability to varying material conditions. Second, regular maintenance and training for operators can significantly reduce downtime and optimize the welding process. By investing in the right technology and workforce development, businesses can harness the full potential of robotic welding, leading to increased productivity and reduced waste.
| Type of Robotic Welding | Technology | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Welding | MIG, TIG, Submerged Arc | Automotive, Aerospace, Structural Steel | High precision, Speed, Consistency |
| Laser Welding | Fiber Laser, CO2 Laser | Electronics, Medical Devices, Automotive | Minimal thermal distortion, Clean welds |
| Spot Welding | Resistance Welding | Automotive manufacturing, Appliances | Rapid production, Strong bonds |
| Plasma Welding | Plasma Arc Welding | Aerospace, Shipbuilding, Pipe welding | High quality welds, Versatility |
| Friction Stir Welding | Solid-State Welding | Aluminum, Aerospace, Automotive | No filler material, Less distortion |
When considering the implementation of robotic welding solutions, several key factors must be evaluated to ensure a successful transition. First and foremost, assessing the specific needs of the welding process is crucial. This includes understanding the types of materials and the complexity of the shapes that will be welded. Different robotic systems may be better suited for certain applications, so aligning the technology with the project requirements can significantly enhance efficiency and output quality.
Another critical factor is the integration of the robotic system within the existing production workflow. It's essential to analyze how the robotic welding equipment will interact with other machinery and processes to avoid bottlenecks. This may involve adjustments to the workflow, employee training, and even modifications in the layout of the manufacturing floor. Additionally, considerations for maintenance and support of the robotic systems should not be overlooked, as a robust service plan will help ensure minimal downtime and optimal performance.
The future of robotic welding and automation in industry is poised for significant advancements as technology continues to evolve. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, robotic welding systems are becoming smarter and more efficient. These systems can now learn from past projects, adapt to new materials, and optimize their processes in real-time, greatly enhancing productivity and reducing errors. This shift not only speeds up production times but also improves the quality of the welds, leading to stronger and more durable products.
Moreover, the trend toward Industry 4.0 is driving the adoption of interconnected systems and smart manufacturing techniques. Robotic welding is at the forefront of this transformation, enabling seamless communication between machines and operators. This interconnectedness allows for better data collection and analysis, enabling companies to optimize their workflows and resource management. As industries face increasing demands for customization and rapid production, the flexibility of robotic welding systems will be essential in meeting these challenges, solidifying their role as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing processes.